MES Systems (Manufacturing Execution Systems): A key specialty of explitia
MES-Class systems (Manufacturing Execution Systems) are undoubtedly one of the core specialties of explitia. This includes solutions based on the AVEVA platform as well as proprietary applications like the Production Portal. By implementing these systems, we support our clients in managing their production processes. But what exactly are MES systems, and why are they so essential?
What are MES Systems?
MES systems are advanced tools that support production management. They act as a bridge between the control layer and the management layer of a production facility. Their primary function is to collect data from machines and production processes, process it, and deliver key insights to those responsible for planning, execution, and production optimization.
With these systems, manufacturing facilities can monitor, analyze, and improve production efficiency in real-time. This is crucial in today’s dynamic industrial environment.
Key functions of MES Systems
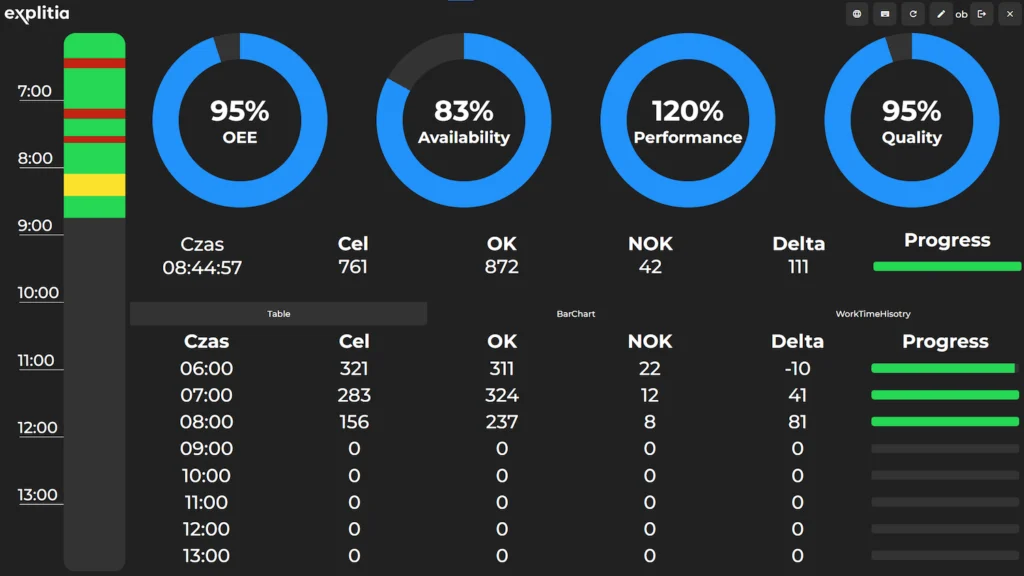
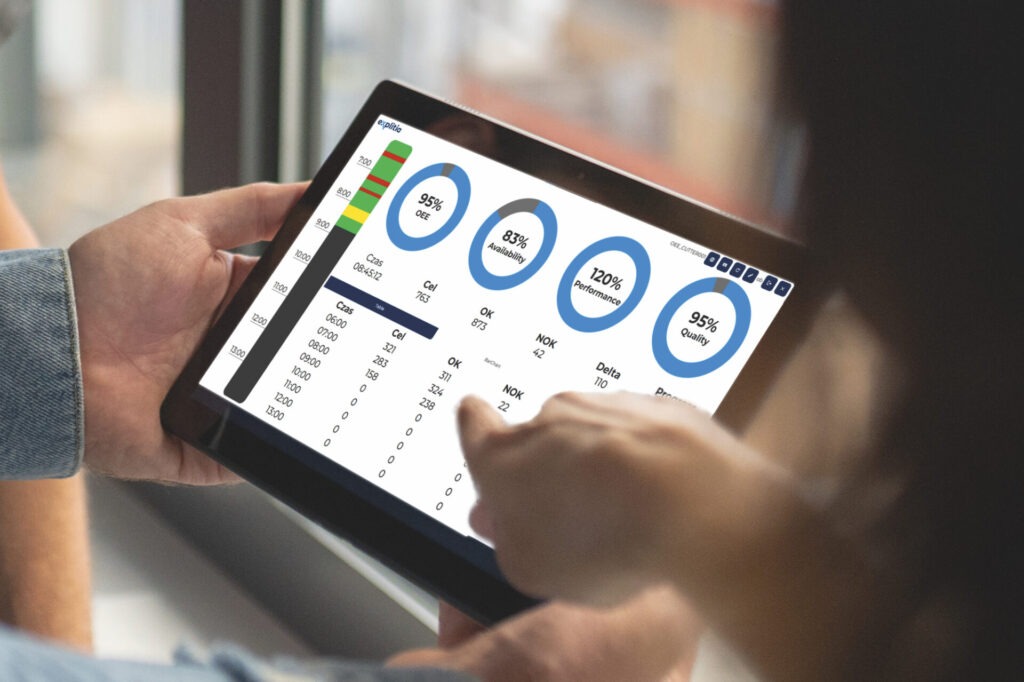
1. Monitoring and calculating OEE
One of the most commonly used performance metrics in production is OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). MES systems enable the automatic collection of data necessary for its calculation, considering three key components:
- Availability – The time a machine is capable of operating,
- Performance – The production speed compared to the planned efficiency,
- Quality – The percentage of good products out of the total production.
This automation allows real-time monitoring of machine efficiency and helps identify potential issues in production processes. Read more about OEE.
2. Traceability systems (production tracking)
Traceability refers to the ability to track the entire production process, from the components used in manufacturing to the final product. MES-Class systems record key data, including:
- Which components were used in the production process?
- The machine parameters set during production?
- When and by whom the product was manufactured?
- The origin of raw materials and components used to create the final product
This enables detailed tracking of the production history for each item, which is invaluable for quality verification or identifying potential defects. Read more about traceability
3. Automated execution of production orders
MES systems integrate with higher-level systems like ERP (e.g., SAP), enabling the automatic processing of production orders. These orders are then assigned to the appropriate machines, and production progress is automatically reported back to the ERP system. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, significantly reducing the risk of errors. Read more about MES and ERP integration.
4. Support in production planning
While MES-Class systems are not primarily designed for production planning, they offer tools that support the optimization and automation of task sequences. By accounting for factors such as downtimes, changeovers, and other variables, MES systems help operators make better scheduling decisions. Read more about production planning and scheduling.
Integration with machines and communication
One of the challenges in implementing MES systems is integrating them with diverse production machinery. Open communication protocols, such as OPC, enable seamless data exchange between the system and machines. Additionally, effective work with controllers, such as those from Siemens, ensures efficient integration of the solution into the infrastructure.
Example of MES application: OEE and Traceability
Consider a simple scenario: A machine produces components with a planned output of 100 units per shift. Using an MES system, you can monitor the number of units produced, machine operating time, and product quality. The system automatically calculates the OEE and generates reports to identify areas for improvement.
For advanced needs, like traceability, the system records not only the number of items produced but also details about components, production parameters, and machine history. This enables automatic verification of whether a product meets all requirements before it reaches the customer.

Why are MES-Class Systems crucial for modern manufacturing?
MES systems play a pivotal role in modern production facilities by combining automation with intelligent management. They not only collect data but also transform it into valuable insights that support decision-making at all organizational levels. With MES systems, companies can monitor and optimize production processes in real-time, significantly improving efficiency and competitiveness.
Key benefits of implementing MES Systems:
1. Data automation
MES systems eliminate manual data entry by automatically collecting, analyzing, and delivering information to higher-level systems like ERP. This minimizes errors and speeds up order processing.
2. Production Optimization
By identifying bottlenecks and monitoring metrics such as OEE, MES systems help enhance machine efficiency and enable targeted improvements.

3. Improved quality
Traceability features allow MES-Class systems to track every stage of production, ensuring rapid identification and resolution of potential quality issues.
4. Seamless integration
MES systems bridge the gap between shop-floor control and enterprise-level management systems like ERP, ensuring comprehensive operational visibility.
5. Predictive planning
Advanced MES features support predictive maintenance and optimized scheduling, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing unplanned downtime.
In today’s dynamic market, MES systems are the foundation of modern manufacturing, driving efficiency and providing companies with tools to gain a competitive edge globally.
If you’re wondering how an MES-Class system could benefit your company, feel free to reach out to us – we’re happy to provide advice and share our expertise. 😊
Write to us!
Are you looking for IT systems for your machinery park? Want to digitize your facility? Schedule a free consultation today!


