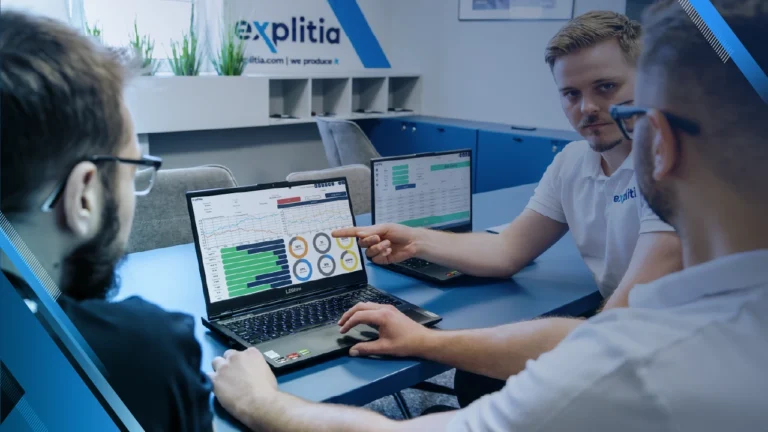
An ERP system (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a comprehensive software solution used to manage a company’s resources by integrating all core business areas into one consistent whole. The main objective of an ERP-type system is to streamline the flow of information between different departments within an enterprise and to provide a unified database available in real time.
In a world where the number of processes and resources grows daily, and manual data management becomes inefficient, ERP software is becoming a fundamental working tool. But should every enterprise implement ERP-class software? How does ERP differ from other solutions such as MES? And what benefits can be expected from investing in ERP IT systems?
All these questions are answered in this article.
ERP system – what does it mean in practice?
ERP software operates like a central database that collects and processes information from all areas of the business. Thanks to this solution, data entered in one department is immediately available to others, eliminating duplication and ensuring data timeliness.
The ERP system collects, processes, and provides data from areas such as:
- finance and accounting,
- human resource management,
- production,
- sales and marketing,
- logistics and supply chain management,
- customer service,
- project management,
- business analytics.
Main functions of an ERP management system
The basic functions of ERP software include:
- data integration in one place,
- Material Requirements Planning (MRP),
- monitoring operational effectiveness (including Overall Equipment Effectiveness, OEE),
- automating information flows,
- supporting decision-making through advanced analytics.
In practice, this means that every decision is based on up-to-date, verified data, not on intuition or outdated reports.
Working in an ERP system involves daily interaction with a tool that collects, processes, and analyzes data from various departments of the enterprise. Every operation – from issuing an invoice, through receiving a delivery, to executing a production order – is recorded in one system.
How soes ERP work in a manufacturing plant?
An ordinary day, yet completely different thanks to ERP. Let’s see how a manufacturing plant works with the support of Enterprise Resource Planning. The sales department enters a customer order. The system automatically checks the availability of materials in the warehouse (thanks to the ERP warehouse module), starts the raw material ordering process (if necessary), and forwards the order to the production department. Accounting immediately registers the order in the books, and logistics plans the delivery.
This entire process takes place in one system, without the need for manual information transfer between departments.

The most important modules of an ERP IT system
ERP-class systems feature a modular structure, which means a company can implement only those components necessary for its operations. At the same time, all modules are integrated, eliminating the need to enter the same data multiple times and ensuring data consistency across the organization.
Let’s take a closer look at the key ERP system modules.
1. Finance and accounting module
This is the heart of any ERP system. It manages the company’s finances and includes elements such as:
- general ledger,
- accounts payable and receivable,
- budgeting and controlling,
- fixed asset management,
- tax settlements,
- financial reporting.
explitia ERP offers advanced analytical accounts for managers, enabling detailed financial control and better strategic planning.
2. Human Resource (HR) management module
Supports processes related to employment and employee service, including:
- HR administration,
- payroll processing,
- working time management,
- recruitment and onboarding,
- employee development and training,
- periodic evaluations,
- employee self-service.
3. Production management module
Crucial for manufacturing companies, it enables effective planning and control of the production process, including:
- material requirements planning,
- production scheduling,
- quality control,
- management of production resources,
- monitoring production efficiency (OEE).
4. Supply Chain Management (SCM) module
Covers all aspects related to the flow of goods:
- procurement management,
- warehouse management,
- inventory control,
- logistics and transport,
- supplier relations.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) module
Supports customer relationship management. Includes:
- customer database,
- sales management,
- marketing,
- after-sales service,
- customer behavior analysis.
6. Project management module
Enables effective planning and implementation of projects. Improves:
- task and resource planning,
- progress tracking,
- project budgeting,
- reporting.
7. Business intelligence module
Provides data analysis tools and supports decision-making through:
- advanced reports and dashboards,
- predictive analytics,
- KPI indicators,
- data visualization.
Contact us
If you’re wondering how to optimize your production, you’re in the right place. Contact us to find out which solutions will work best for your business.
Benefits of implementing an ERP system
Implementing an ERP system brings numerous benefits to companies, translating into increased operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Let’s explore the most important ones.
1. Increased operational efficiency
ERP systems automate many repetitive processes, reducing the time needed to perform routine tasks.
2. Higher data quality and better business decisions
A shared database eliminates discrepancies between departments. With access to current and consistent data, management can make more accurate business decisions.
3. Inventory management optimization
ERP enables precise material requirements planning, reducing inventory levels and related costs while minimizing the risk of stock shortages that could disrupt production.
4. Improved production efficiency
Implementing an ERP system can significantly improve the OEE indicator. The system allows for better production planning, downtime reduction, and optimized use of production resources.
5. Improved customer service
With integrated customer, order, and product data, customer service representatives have immediate access to all necessary information, resulting in faster and more professional service and increased customer satisfaction.
6. Reduced operating costs
Process automation, data duplication elimination, and more efficient resource management lead to measurable savings, including administrative and operational costs.
7. Business growth support
Modern ERP systems are scalable and flexible, allowing them to adapt to the growing needs of the company. ERP solutions use advanced technologies such as machine learning and predictive analytics to support strategic business development.
8. Compliance with Regulations and Standards
ERP systems facilitate compliance with legal and industry requirements through automatic updates and built-in compliance control mechanisms.
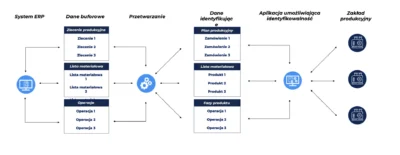
ERP integration with other systems
In a modern business environment, ERP systems rarely function as isolated solutions. To fully leverage their potential, they are often integrated with other systems and tools. One of the most important integrations is with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems).
MES – a complementary solution to ERP
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is an IT system focused on managing and controlling production processes in real time. Unlike ERP, which covers the company as a whole, MES focuses exclusively on production, offering more detailed and specialized tools for this area.
MES systems handle aspects such as:
- detailed production planning and scheduling,
- production resource dispatching,
- product tracking and genealogy,
- quality management in production processes,
- data collection directly from production machines,
- detailed production efficiency analysis (OEE).
It is worth noting that ERP systems may not suffice in every company, especially in manufacturing enterprises with complex production processes. In such cases, implementing MES as the core production management tool, supplemented by selected ERP modules, may be a better solution.
Five benefits of ERP and MES integration
The integration of these two systems brings numerous benefits:
- Complete Business Insight – ERP provides a broad business overview, while MES delivers detailed data on production processes.
- Elimination of Duplicate Data Entry – Information entered in one system becomes automatically available in the other.
- Optimized Production Planning – Real-time data from MES enables more accurate planning within the ERP system.
- Improved Quality Control – MES quality data can be integrated into ERP’s logistics and customer service processes.
- Accurate Cost Calculation – Detailed data from MES on material usage and labor time improves ERP-based production cost estimation.
ERP Implementation – best practices
Implementing an ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning. It typically involves several key stages:
- Needs and requirements analysis.
- Selecting the appropriate solution.
- Implementation planning.
- System configuration and customization.
- User training.
- Testing – pilot program.
- Full deployment and post-implementation support.
When to implement an ERP system
The right time to implement ERP depends on many factors, such as company size, process complexity, and industry. However, some indicators suggest a company may need an integrated management system:
1. Problems with information flow
Inefficient communication between departments or duplicate data entry into various systems.
2. Increasing headcount
As employee numbers grow, spreadsheets and emails become insufficient.
3. Difficulty accessing real-time data
Management lacks up-to-date performance data or waits too long for reports.
4. Inventory management issues
Frequent stockouts or overstocking signal the need for better materials planning.
5. Inefficient business processes
Employees spend too much time on repetitive, manual tasks that could be automated.
6. Business growth
Plans to expand into new markets or introduce new products/services call for a scalable ERP platform.

ERP applications across industries
ERP systems are used across nearly every sector, though implementation varies by industry. Key applications include:
Industrial manufacturing
In manufacturing, an ERP system supports production processes through:
- material requirements planning (MRP),
- machine and process performance tracking (OEE),
- quality management and supply chain optimization.
Retail and E-commerce
Most representatives of the commercial sector use ERP-class software that focuses on:
- multichannel inventory management,
- demand forecasting and restocking automation,
- integration with sales platforms.
Financial services
If you work in the financial sector, you may also encounter ERP systems being used for:
- automated accounting processes,
- regulatory compliance,
- advanced business analytics.
Other sectors
An ERP management system also supports:
Healthcare: Patient data, resource planning, and insurance billing
Construction: Project planning, cost control, subcontractor management
Logistics: Route optimization, shipment tracking, profitability analysis
Public Sector: Budget management and integration with e-government systems
Modern ERP systems are increasingly specialized, offering sector-specific solutions.
The explitia ERP system is a comprehensive enterprise management solution that integrates all key business processes in project- and service-oriented companies.
Implementing ERP management software brings numerous advantages. Depending on the specific solution and industry, these can include: improved operational efficiency, better data quality and decision-making, optimized inventory management, and enhanced production effectiveness. At the same time, it’s important to remember that in many production plants, a standalone ERP system may not be enough. For detailed control of manufacturing processes, integrating ERP and MES solutions is often the best approach.