The concepts of ERP and MES may resemble cryptonyms for secret intelligence missions, yet these names are commonly heard in the industrial sector.
Modern manufacturing demands precise planning, control, and data analysis. To meet these challenges, companies increasingly turn to advanced IT systems like ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and MES (Manufacturing Execution System). While both systems aim to streamline manufacturing processes, their functionalities differ. In this article, we’ll explain the roles of each system and how their combined use can optimize production processes and elevate your company to the level of Industry 4.0.
ERP and MES: Similar yet completely different
ERP – The heart of the enterprise
The ERP system (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a comprehensive tool for managing a company. Its purpose is to integrate all key business processes, such as:
- Finance (managing accounting, invoices, payments, etc.),
- HR (managing personnel, payroll, recruitment),
- Production (production planning, inventory management),
- Logistics and Sales (managing orders, customer relationships).
MES – The brain of production
MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is a specialized tool that focuses exclusively on production processes:
- Production Planning (creating detailed production schedules, managing production orders),
- Production Monitoring (tracking production progress in real-time, collecting data on machine and employee performance, resource usage, and material consumption),
- Quality Control (ensuring products meet quality requirements).
What should be in ERP and what in MES?
Each year, the line between ERP and MES blurs slightly. Vendors of both systems introduce features that were once exclusive to one or the other. ERP offers increasingly detailed production modules, while MES is enhanced with business functionalities. Moreover, there is a wide range of solutions on the market, from major players and mass-market platforms (e.g., Microsoft Dynamics or SAP) to more sector-specific, niche solutions tailored to specific businesses. As a result, it is challenging to define a clear division of roles between MES and ERP.
This blurring of boundaries can lead to dilemmas during system implementation – what should be included in ERP, and what should be in MES?
Generally speaking, in the production process, ERP initiates an order by defining general parameters (e.g., product type, quantity, delivery deadline), while MES handles the details, such as selecting the appropriate materials and scheduling machine work.
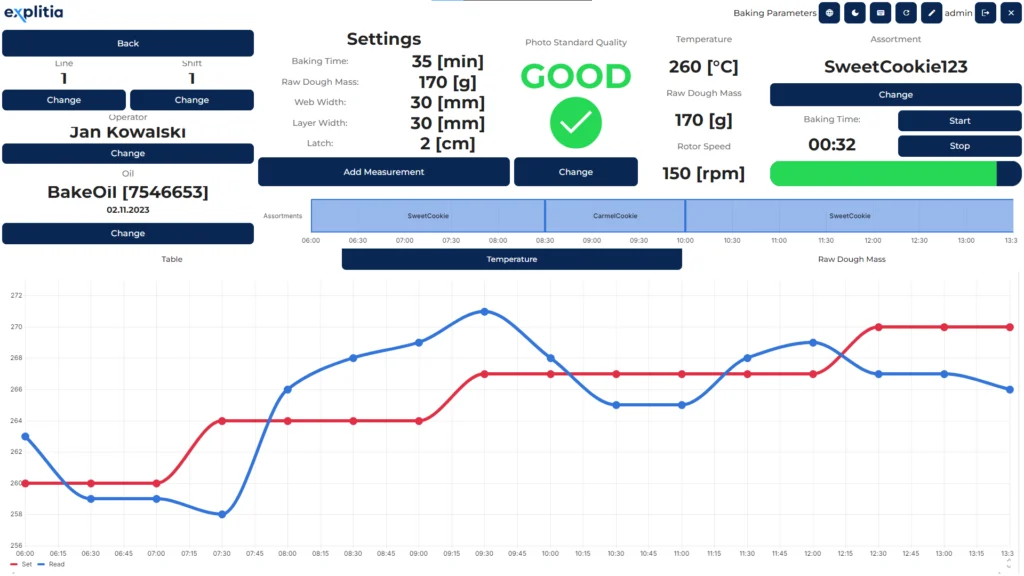
When to implement ERP and when to implement MES systems?
In an ideal scenario, both systems should be implemented simultaneously. Why? Coordinated planning ensures a clear division of responsibilities between ERP and MES, minimizing the risk of overlapping functionalities.
However, if a choice must be made, the decision should consider your most pressing needs and what will work best in your specific case. Each solution has its own advantages.
ERP First
ERP forms the foundation for managing the entire enterprise, connecting all departments. It supports the automation of processes such as invoicing, customer order management, and HR-related activities.
MES First
From another perspective, implementing MES is less complex as it focuses solely on production. It’s often worth starting with MES, as it allows for a faster optimization of shop floor processes. Once MES is in place, integrating it with ERP becomes easier.
How ERP and MES collaborate in a production facility
ERP and MES systems should work closely together, like a relay team. Here’s how:
1. An order is received in the ERP system.
2. ERP generates a production order, setting general parameters (e.g., quantity, type of product, delivery deadline).
3. ERP passes the order to MES.
4. MES plans production in detail, selecting machines, materials, and scheduling work.
5. During production, MES monitors progress in real-time.
6. After completion, MES sends data back to ERP, which updates inventory, records costs, and notifies the customer of product readiness.
This bidirectional exchange of data between ERP and MES ensures smooth and efficient processes. MES provides detailed shop floor insights, while ERP translates them into actionable business data.
Benefits of ERP and MES integration
As mentioned, ideally, both ERP and MES should be implemented. What are the benefits of their integration?
• Improved control over production processes – MES monitors production in real-time, while ERP offers a comprehensive financial and logistical overview.
• Enhanced efficiency and reduced production time – thanks to MES planning and ERP automation.
• Cost reduction – optimized production processes and automated data entry reduce material waste.
• Optimal resource utilization.
• Better collaboration between departments.
The collaboration of ERP and MES is essential for modern manufacturing facilities. ERP manages the business, while MES focuses on production details. While each system specializes in different areas, their integration delivers tangible benefits – from increased process transparency and cost optimization to faster order fulfillment. Regardless of company size, investing in both systems is not an expense but a step toward Industry 4.0.


